
What is the digestive system?
The Complex Process Beyond Food Breakdown and Elimination
The human digestive system is a remarkable and intricate network of organs, enzymes, and chemical reactions that work harmoniously to process the food we consume. It’s not just about breaking down your last meal; it’s a crucial process that ensures your body receives the necessary nutrients for optimal function. In this blog, we will delve into the mechanics of your digestive system, explore the roles of its various components, and discuss ways to enhance its efficiency.
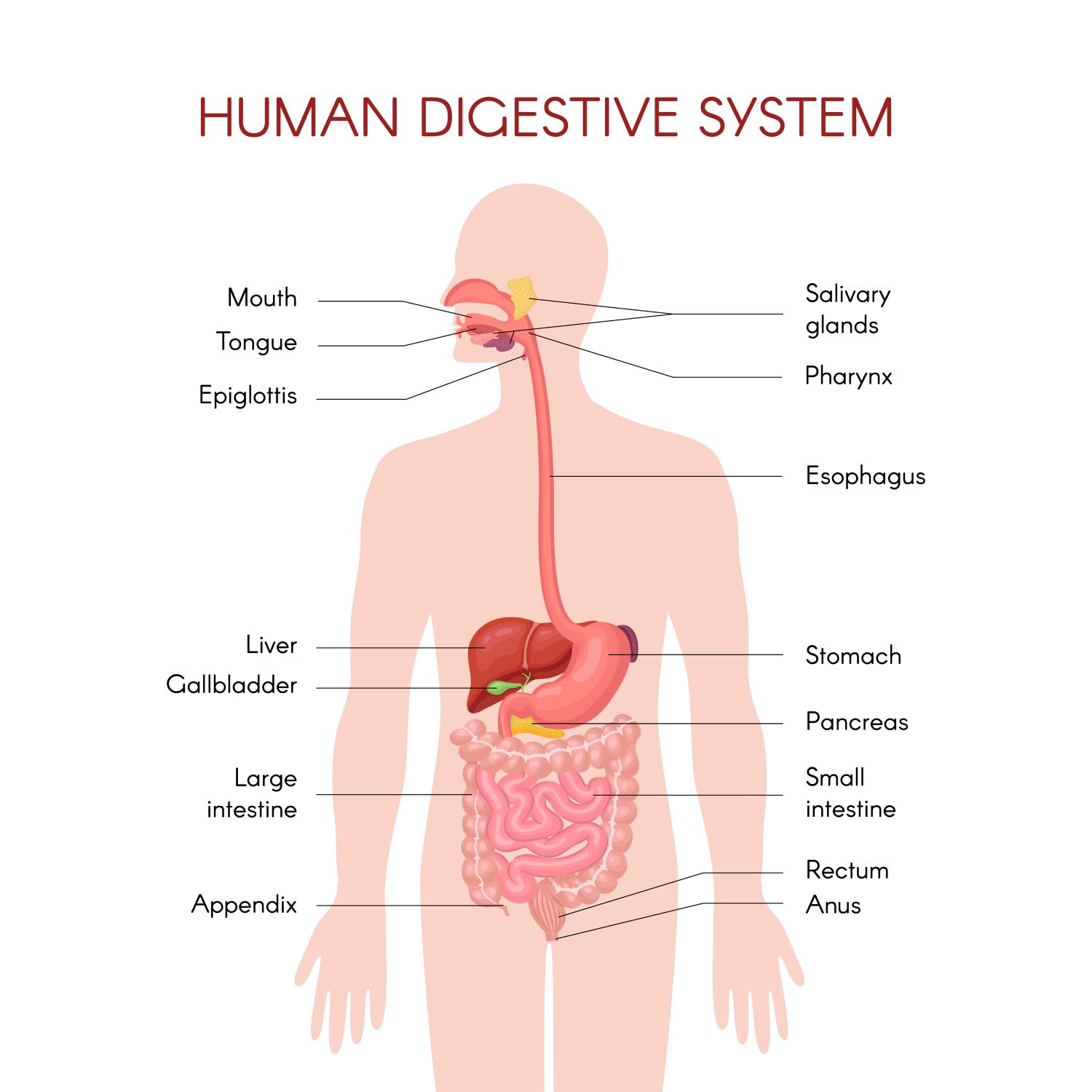
What are the organs in the digestive system?
A Team Effort – Your digestive system comprises several organs, each with a specific role. Each of these organs plays a crucial role in the digestion process, with intricate mechanisms designed to ensure the proper breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Mouth: Digestion initiates here with the mechanical breakdown of food through chewing, and the chemical breakdown begins with the action of saliva.
Esophagus: This muscular tube transports chewed food to the stomach through a coordinated process called peristalsis.
Stomach: The stomach’s muscular walls contract and churn the food, mixing it with gastric juices, which contain hydrochloric acid (HCl) and various enzymes, most notably pepsin (used for protein breakdown). Not only that, the acidic environment of the stomach is hostile to many harmful bacteria that may come with food and drinks.
Small Intestine: This lengthy tube is where the bulk of nutrient absorption occurs, thanks to tiny finger-like structures called villi. This is the most important organ in digestion. It also helps transport waste products into the large intestine for elimination.
Liver and Gallbladder: These organs provide bile, essential for emulsifying and digesting fats.
Pancreas: It secretes digestive enzymes and hormones, such as insulin, to regulate blood sugar levels.
Large Intestine (Colon): In the colon, water is absorbed from undigested food, and waste is formed.
Rectum and Anus: The final stages involve the elimination of waste from the body.
Therefore, the 3 main functions of the digestive system are breakdown of food, nutrient absorption, and elimination of food waste.
How long does food take to digest?
After you eat, it takes about 6 to 8 hours for food to pass through your stomach and small intestine. Food then enters your large intestine (colon) for further digestion, absorption of water and, finally, elimination of undigested food. It takes about 36 hours for food to move through the entire colon.
The Chemical Production: Role of Enzymes
Enzymes are key players in the digestion process. They are specialized proteins that facilitate chemical reactions in the body. Digestive enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and protease, are responsible for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively. Without these enzymes, digestion would be severely impaired, and nutrients wouldn’t be absorbed effectively.
Dysregulation of Enzyme Production Led To…
When the production of these essential enzymes is disrupted or insufficient, it can lead to many digestive problems. Common symptoms include bloating, gas, indigestion, and nutrient deficiencies. It’s as if the orchestra of your digestive system is missing some musicians, and the result is a discordant melody.
Other factors that can impair the digestive system:
Leaky Gut Syndrome: It’s a condition where the lining of the small intestine becomes more permeable or “leaky” than it should be. In a healthy digestive system, the intestinal lining acts as a barrier, selectively allowing nutrients and substances necessary for your body to pass through while preventing harmful substances like bacteria, toxins, and undigested food particles from entering the bloodstream. In the case of Leaky Gut Syndrome, this barrier function is compromised, allowing larger molecules to pass through the intestinal wall. This can trigger an immune response and lead to a variety of health issues.
Dysbiosis: An imbalance in the gut microbiota. In a healthy gut, there is a delicate balance between beneficial and potentially harmful microorganisms. Dysbiosis occurs when this balance is disrupted, leading to an overgrowth of harmful microbes.
Candida Overgrowth: Candida is a type of fungus or yeast that normally resides in small quantities in various parts of the body, including the mouth, throat, gut, and genital area. Candida plays a role in digestion and maintaining a healthy balance of microorganisms in these areas. An overgrowth of the yeast Candida in the gut can cause digestive disturbances and other health issues.
How can these happen?
Diet: A diet high in processed foods, and sugar, and low in fiber can potentially harm the gut lining, and gut bacteria, and a lack of dietary fiber may reduce the diversity of beneficial gut bacteria.
Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress can negatively impact the gut through various mechanisms, including alterations in gut motility, blood flow, and immune function. Stress hormones may also affect the integrity of the gut lining.
Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotics.
Infections: Gastrointestinal infections, such as bacterial or parasitic infections, can damage the intestinal lining and disrupt its barrier function.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and pollutants, may contribute to gut inflammation and permeability.
Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can irritate the intestinal lining and contribute to increased permeability.
Autoimmune Diseases: Certain autoimmune diseases, such as celiac disease and type 1 diabetes, are associated with increased intestinal permeability.
Chronic Inflammation: Conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can lead to gut barrier dysfunction.
How to Improve Your Digestion
To maintain a healthy digestive system and optimize its functionality, consider the following:
Eat Mindfully: Chew your food thoroughly and savor each bite.
Fiber-Rich Foods: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet to support digestive health. This fiber rich foods act as prebiotics which help maintain a balance gut microbiome.
Eat enzymes rich food:
Sauerkraut and kimchi contain protease, lipase, and amylase which can help break down protein, fat and carbohydrate.
Pineapple is high in bromelain, a family of enzymes that includes peroxidase, acid phosphatase, cysteine proteinases, and proteolytic (protein-digesting) enzymes.
Kefir is a yogurt-like fermented drink that contains lipase, protease, and lactase enzymes. Kefir may help with lactose intolerance and is rich in probiotics that improve overall gut health.
Miso is made from fermented soybeans and contains several digestive enzymes, including lipases, proteases, amylases, and lactases. Miso can thus help ease digestion and relieve symptoms of irritable bowel disease.
Raw honey contains a wide range of digestive enzymes, including diastase, amylase, invertase, and protease. Diastase helps digest starch, amylase breaks down starch into sugars, invertase breaks down sucrose, and protease breaks down protein into amino acids.
Stay Hydrated: A well-hydrated body aids in smooth digestion and elimination.
Probiotics: Consider including probiotic-rich foods or supplements to promote a balanced gut microbiome. Foods these days contain substances that deplete the microbiome.
Stress Management: Stress can negatively impact digestion. Your digestion happens in the parasympathetic nervous system which means when you feel relaxed and safe. So, explore stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness breathing or fake yawning before a meal.
In conclusion, your digestive system is a complex and vital component of your overall health. Understanding its inner workings and taking steps to promote its optimal function can lead to improved digestion and a healthier you.
